All You Need To Know About Learning Styles
No one learning style fits all students, Every student has their own strategy that aids them to remember information more efficiently while studying. Some kids learn while they take notes; some make diagrams; some prefer to listen to the teacher attentively, etc.
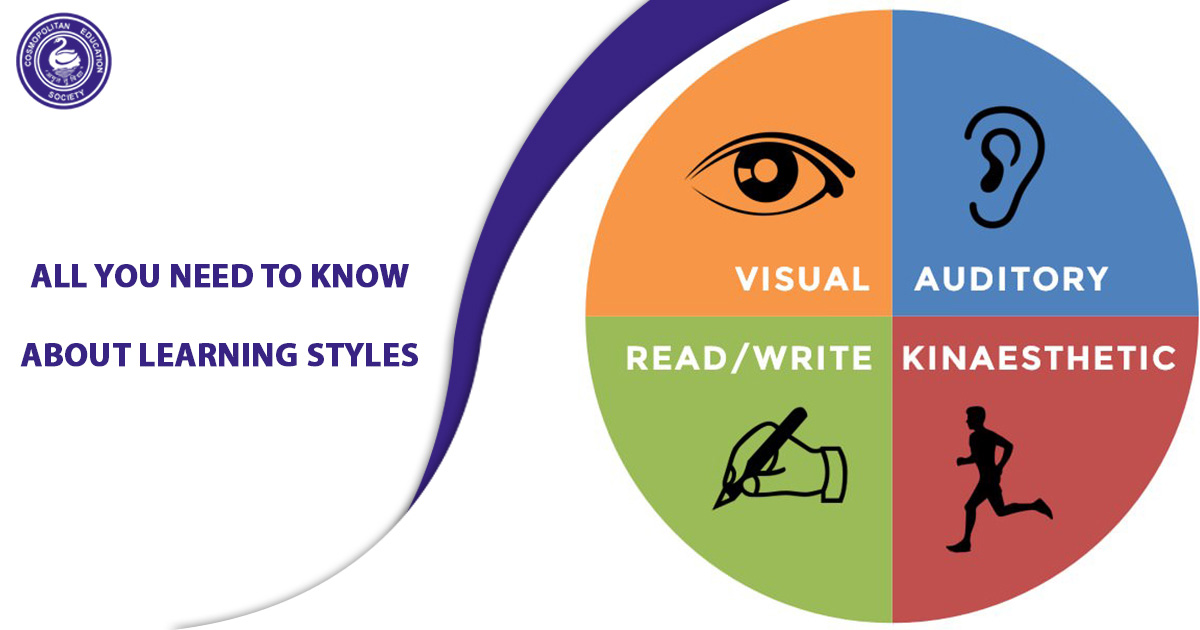
Let’s look at the 4 different types of learning styles
It is a studied and proven fact that scientists have for years tried to understand the best ways students learn through research. One of the popular theories, in today’s world, is the VARK model. This model identifies four types of learners: Visual, Auditory, Reading and Kinesthetic.
Most people are a combination of these four styles, but all of them have that 1 predominant style that makes them grasp information to last long. Each of these styles has a complementary way of teaching. Now, let’s see the characteristics each of these styles entails and how best to make use of them.
Visual Learning Style:
Visual learners are individuals who prefer to take in their information visually – be it through maps, graphs, diagrams, charts, and many other visual learning aids. However, they don’t necessarily respond similarly to photos or videos, compared to information gained using different visual aids such as patterns and shapes.
The best way to teach visual learners is by showing them the relationship between different ideas visually. For instance, when explaining a scientific process, it can be best done by using a flow chart.
Auditory Learning Style:
Auditory learners are individuals who learn better when they take in information in the auditory formate when it is heard or spoken. They are prone to organising their ideas after speaking, rather than thinking ideas through before. Since, to them, saying things out aloud helps them understand the concept. They could grasp learning content by either hearing a 2nd person or by reciting information aloud themself. The idea is concepts should reach their ears.
Auditory learners learn best when information is presented to them via strategies that involve talking, such as lectures and group discussions. You can ideally ask them to repeat or teach back a concept for reinforcement of learning. They highly get benefited from recordings of the lectures, group activities that require classmates explaining ideas, etc.
Reading/Writing Learning Style:
Reading/writing learners consume information best when it’s in words, either by writing it down or by reading it. To them, the text is more powerful than any kind of visual or auditory representation of a concept. These individuals usually perform very well on written assignments.
There are different ways to get a reading/writing learner to engage and understand a certain lesson. For example, it would be best to have them describe charts and diagrams by written statements, take written quizzes on the topics, or give them written assignments.
Kinesthetic Learning Style:
Kinesthetic learners are individuals who prefer to learn by doing things on their own. They get thrilled by hands-on experience. They are usually more in touch with reality and more connected to it, which is why they require using tactile experience to understand something better.
The best way to present new information to the person with a dominant kinesthetic approach to learning is through personal experience, practice, examples, or simulations. For instance, they can remember an experiment by recreating it themselves.
Additional Types of Learning Styles
Now that we have discussed the 4 most prevailing learning styles that have been around for a while, it’s time we can explore additional learning styles which are lesser known. It is important to note that not everyone agrees on the types of learning styles, their names, or even their number. Recent studies and theories from psychologists and experts in the field suggest that there are anywhere between 3 to 170 different types of learning styles.
A few other types of learning styles are below:
Logical/analytical learners: As the name suggests, analytical learners depend on logic and analytical skills to understand a particular subject thoroughly. These types of learners search for connections, causes, patterns, and results in detailed learning. A teacher can engage and motivate analytical learners by posing questions that require interpretation, using material that activates problem-solving skills and stimulating students to reach conclusions based on facts or reasoning.
Social/linguistic learners: These types of learners favour educational lessons that include peer work or participation. Social/ linguistic learners get mainly two benefits out of this learning method: socializing (which they love) and a better understanding of a subject. Teachers can motivate these types of learners by using role-playing, group activities, encouraging student interaction, etc.
Solitary learners: Also highly known as solo learners, these students are the opposite of social learners. Solitary learners prefer to study alone without having to interact with other learners. Individual work/projects is a solo student’s forte. Teachers can help these types of learners by using activities that require individual work (including keeping a diary) and problem-solving skills, recognizing a student’s individual accomplishments, etc.
Nature learners: These types of learners flourish when in contact with nature. A nature learner’s ideal study environment is a calm and relaxing environment. If we had to compare nature learners with another type, it would be tactile learners. The only difference is the nature part of this deal, as nature learners need to be outside to learn better. While learning in nature may not always be possible, teachers can still nurture this learning style in students by assigning hands-on activities, having classes outdoors when possible, and using nature examples when explaining a new lesson.
Summing up:
Since the way someone best consumes information can be a deciding factor in their academic success, understanding what kind of learner they are is vital. You can do this by trying all four methods of learning, and then deciding which one helps you remember best. Once you know what kind of style fits you, you can tailor your studies to fit your needs.
Though it is easier for one individual to understand and incorporate a specific learning style to get better results, it is not that easy for a teacher with, say, 20 students in one classroom. At Harshad Valia International School, teachers design the learning schedule such that a perfect blend where all 4 styles are incorporated throughout the day. Additionally, here is an interesting blog on tips to ensure your child gets most of the curriculum you may want to read up on.
